A vulnerability attack using PoC
The AhnLab Security Intelligence Center (ASEC) has issued a critical warning for all users of HTTP File Server (HFS): a recently disclosed remote code execution vulnerability (CVE-2024-23692) is actively being exploited by malicious actors. This vulnerability allows attackers to remotely execute commands on unpatched HFS servers, leading to a range of malicious activities.
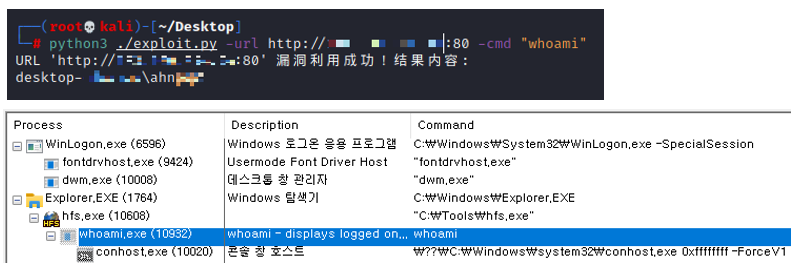
Following the public disclosure of CVE-2024-23692, a proof of concept (PoC) was quickly made available, demonstrating how attackers could exploit the vulnerability. AhnLab’s monitoring through the AhnLab Smart Defense (ASD) infrastructure has detected numerous instances of this vulnerability being exploited in the wild.

The attack process typically begins with the initial infiltration, where threat actors use commands such as “whoami” and “arp” to gather system information. Subsequently, they create hidden backdoor accounts to establish remote desktop connections (RDP), enabling persistent access to the compromised system. To prevent detection by other malicious actors, attackers often terminate the HFS process once their activities are complete.
ASEC has observed a variety of attacks targeting HFS servers, including:
- Cryptomining: Installation of XMRig, a Monero cryptocurrency miner, to harness victims’ computing power for illicit profit.
- RATs and Backdoors: Deployment of Remote Access Trojans (RATs) like Gh0stRAT, PlugX, and XenoRAT, granting attackers persistent control over compromised systems.
- Information Theft: Infiltration of GoThief malware, which exfiltrates sensitive data via Amazon AWS.
Worryingly, ASEC has identified LemonDuck, a notorious threat actor known for exploiting vulnerabilities, among the attackers targeting HFS.
What You Can Do
- Patch Immediately: Update your HFS software to the latest version, which includes a fix for CVE-2024-23692.
- Check for Compromise: If you are running a vulnerable version, investigate your system for signs of unauthorized access or suspicious activity.
- Strengthen Security: Consider implementing additional security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and strong passwords, to protect your HFS server from future attacks.