npq
safely* install packages with npm/yarn by auditing them as part of your install process.
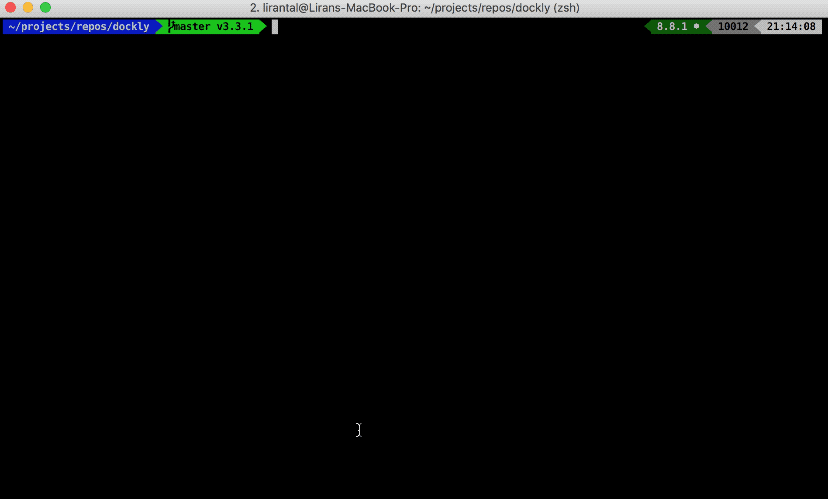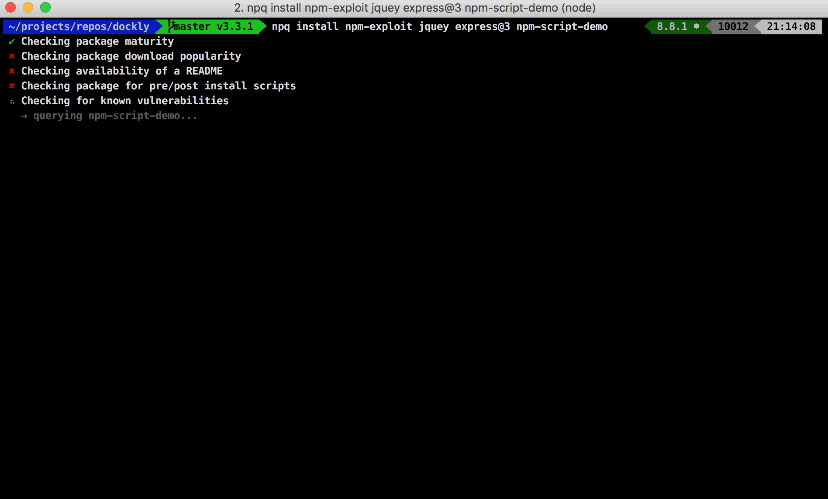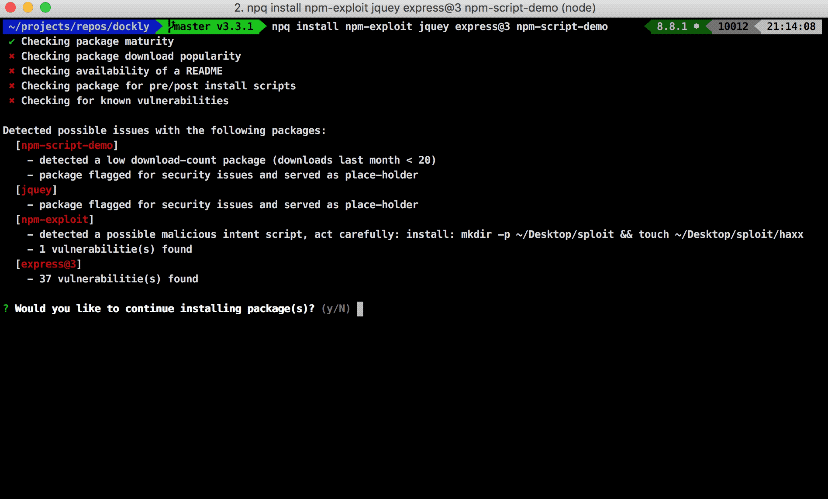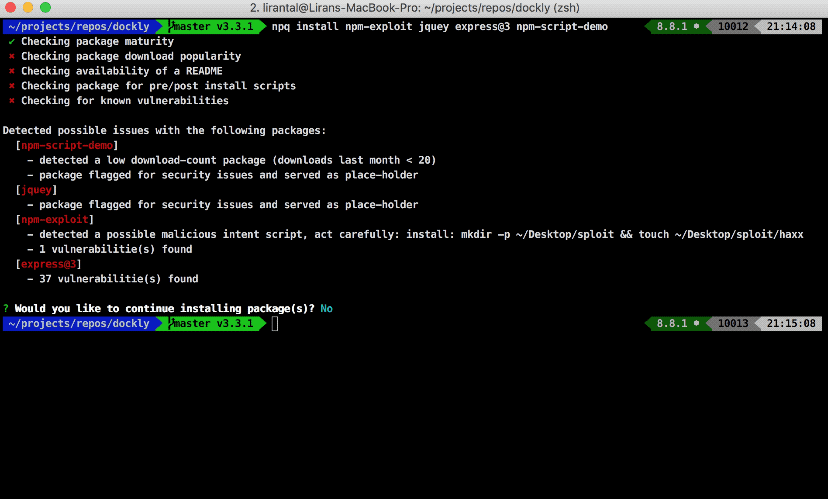
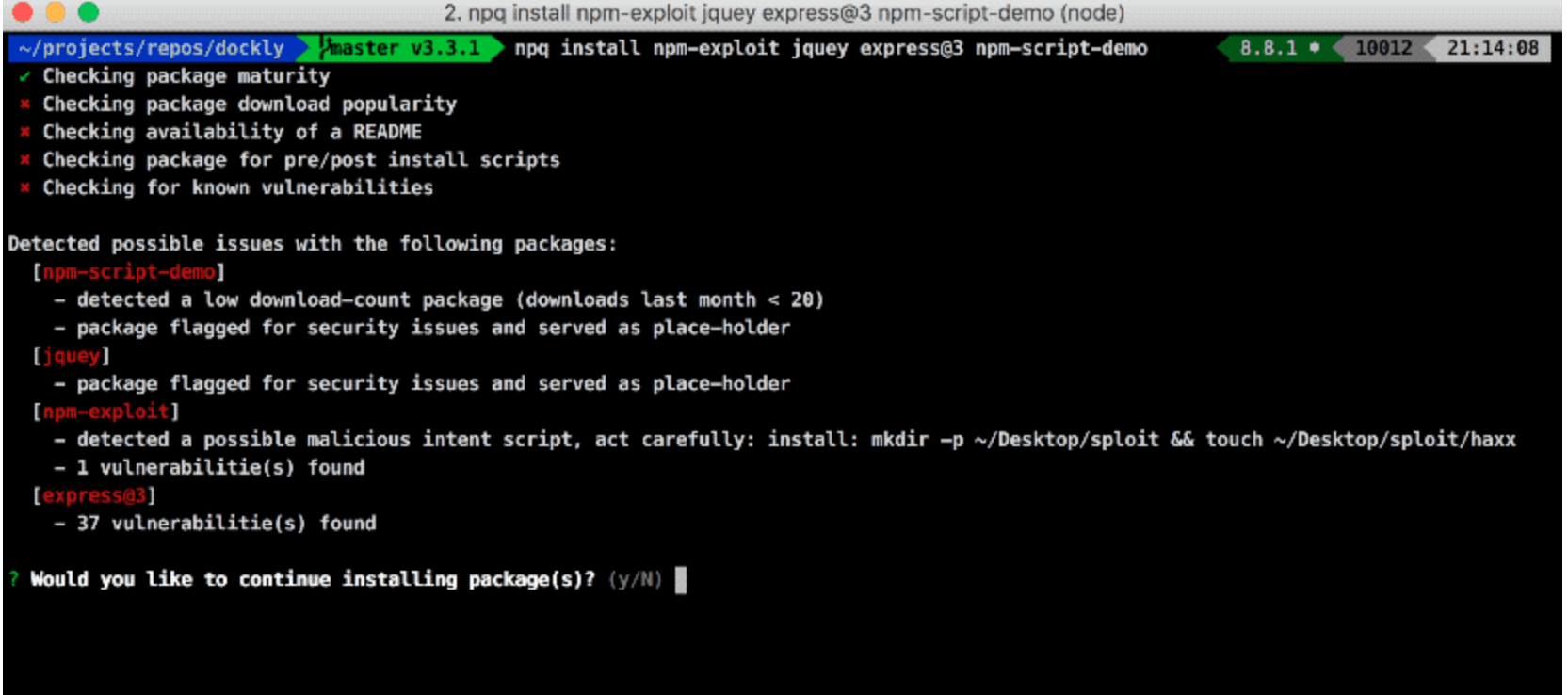
npq will perform the following steps to sanity check that the package is safe by employing syntactic heuristics and querying a CVE database:
- Consult the snyk.io database of publicly disclosed vulnerabilities to check if a vulnerability exists for this package and its version.
- Package age on npm
- Package download count as a popularity metric
- Package has a README file
- Package has pre/post-install scripts
If npq is prompted to continue with the install, it simply hands over the actual package install job to the package manager (npm by default).
safely* – there’s no guaranteed safety; a malicious or vulnerable package could still exist that has no disclosure published and passes npq’s checks.
Changelog v2.0.14
Bug Fixes
Install
npm install -g npq
Usage
Install packages with npq:
npq install express
Embed in your day to day
Since npq is a pre-step to ensure that the npm package you’re installing is safe, you can safely embed it in your day-to-day npm usage so there’s no need to remember to run npq explicitly.
alias npm='npq-hero'
Offload to package managers
If you’re using yarn , or generally want to explicitly tell npq which package manager to use you can specify an environment variable: NPQ_PKG_MGR=yarn
Example: create an alias with yarn as the package manager:
alias yarn="NPQ_PKG_MGR=yarn npq-hero"
Note: npq by default will offload all commands and their arguments to the npm package manager after it finished its due-diligence for the respective packages.
Marshalls
| Marshall Name | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| age | Will show a warning for a package if its age on npm is less than 22 days | Checks a package creation date, not a specific version |
| downloads | Will show a warning for a package if its download count in the last month is less than 20 | |
| readme | Will show a warning if a package has no README or it has been detected as a security placeholder package by npm staff | |
| scripts | Will show a warning if a package has a pre/post-install script which could potentially be malicious | |
| snyk | Will show a warning if a package has been found with vulnerabilities in snyk’s database | For snyk to work you need to either have the snyk npm package installed with a valid api token, or make the token available in the SNYK_TOKEN environment variable, and npq will use it |
Disabling Marshalls
To disable a marshall altogether, set an environment variable using the marshall’s shortname.
Example, to disable snyk:
MARSHALL_DISABLE_SNYK=1 npq install express
FAQ
- Can I use NPQ without having npm or yarn?
- NPQ will audit a package for possible security issues, but it isn’t a replacement for npm or yarn. When you choose to continue installing the package, it will offload the installation process to your choice of either npm or yarn.
- How is NPQ different from the npm audit?
- npm install will install a module even if it has vulnerabilities; NPQ will display the issues detected, and prompt the user for confirmation on whether to proceed to install it.
- NPQ will run synthetic checks, called marshalls, on the characteristics of a module, such as whether the module you are going to install has a pre-install script that can be potentially harmful to your system and prompt you whether to install it. Whereas npm audit will not perform any such checks, and only consults a vulnerability database for known security issues.
- npm audit is closer in functionality to what snyk does, rather than what NPQ does.
- Do I require a snyk API key in order to use NPQ?
- It’s not required. If NPQ is unable to detect a snyk API key for the user running NPQ, then it will skip the database vulnerabilities check. We do, however, greatly encourage you to use snyk, and connect it with NPQ for broader security.
Copyright 2017 Liran Tal.
Source: https://github.com/lirantal/